Unlock the Power of Mental Toughness
What sets high achievers apart? Why do some people thrive under pressure while others struggle?
The answer lies in mental toughness—a powerful trait that shapes how we handle stress, challenges, and opportunities.
Leading Mental Toughness academics describe mentally tough individuals as calm, confident, and resilient. They stay composed in high-pressure situations, maintain focus, and have an unshakable belief in their ability to shape their own success. With lower anxiety levels and a natural ability to bounce back from setbacks, they lead in their industries, achieve ambitious goals, and build strong personal and professional relationships.
These individuals don’t just succeed – they make it look effortless. But here’s the secret: mental toughness isn’t just for elite athletes or top executives – it’s a skill anyone can develop.
Want to learn how to strengthen your own mental toughness and unlock your full potential?
Keep reading as we break down the science behind mental toughness, the pros and cons of being mentally tough, and how you can apply these insights to boost your resilience, personal and professional success, and overall work-life satisfaction.
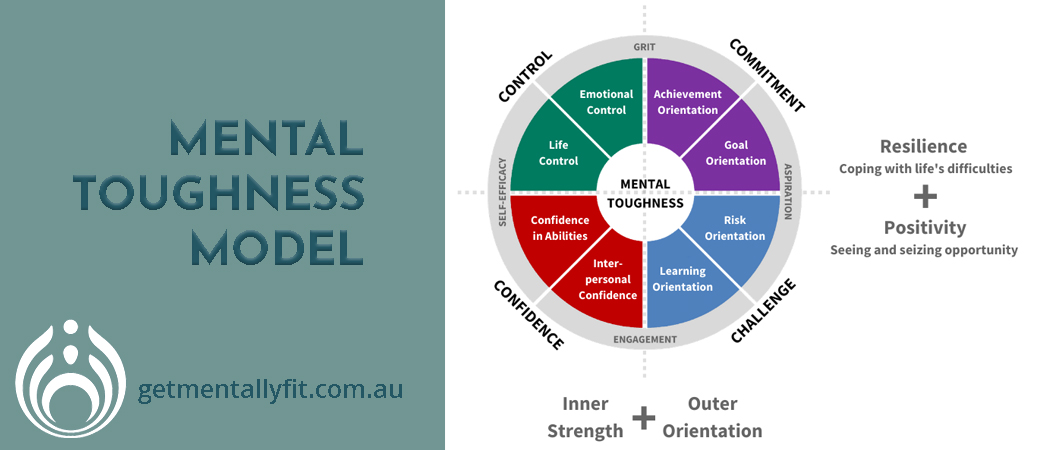
The 8 Factors of Mental Toughness
In a previous article we outlined the four Mental Toughness Constructs: Challenge, Confidence, Commitment and Control – The 4 C’s of Mental Toughness.
Let’s now look at the 8 Factors of Mental Toughness, and how they relate to the 4 C’s:
Challenge: Learning Orientation; Risk Orientation
Confidence: Confidence in Abilities; Interpersonal Confidence
Commitment: Achievement Orientation; Goal orientation
Control: Emotional Control; Life control
1: Learning Orientation
The mentally tough typically approach any situation with the motivating question like, What can I learn? They know that even setbacks are opportunities for learning. A large part of this is having an active exploratory mind and seeking to learn from others.
Often referred to as a growth mindset, this is contrasted with a focus on performance orientation and the question: How can I demonstrate my competence? This is referred to as a fixed mindset.
2: Risk orientation
Risk orientation refers to an individual’s attitude towards change and new experiences. Mentally tough individuals are driven to succeed and push themselves to grow. They typically become leaders in their chosen field.
On the other hand, mentally sensitive individuals see risk as uncomfortable and something to be avoided. In contrast, mentally tough individuals see change as exciting, interesting and they can see the opportunity that new experiences presents for personal development.
3: Confidence in abilities
Mentally tough individuals believe they have the intellectual toolkit (whether it be knowledge, skills, education, and experience) to complete a particular task.
As a result, they tend to approach new tasks or actions with a pragmatism and self-belief that improves the likelihood of successfully completing the task.
4: Interpersonal Confidence
A mentally tough person shows assertiveness – that is, they positively influence others or stand their ground in the face of objections, aggression, or an alternative point of view.
This is an important skill in professional development of self, as a leader or someone who is responsible for their and other’s performance.
5: Achievement orientation
This relates to an individual’s ability to do what it takes to keep a promise and achieve their goals. This requires the individual to have a healthy level of tenaciousness. This means they’re prepared to do what it takes to follow things through, and find targets exhilarating.
This is contrast to a mentally sensitive individual who can shirk commitment in fear of failure. Mentally tough individuals they break projects down into manageable chunks, deliver outcomes on time, and have a strong sense of conscientiousness.
6: Goal orientation
This describes an individual’s preference for goals and targets. Mentally tough individuals set high standards for themselves and others.
Mentally tough individuals like being judged or assessed, accept responsibility, and like ownership, acceptance and responsibility. This is why these individuals tend to be unphased by competition or adversity, and make ideal leaders.
7: Emotional Control
Mentally tough individuals feel they are in control of their life, including their emotions and sense of life purpose. They feel comfortable in their own skin and have a good sense of who they are. This helps them to keep a cool head in pressure situations, and focused when others would find an environment impossibly noisy or stressful.
As a result, the mentally tough are considered to be good leaders and valuable workers in high pressure or stressful roles like working in emergency services. They are also wonderfully calming to others in times of despair.
8: Life Control
Mentally tough individuals feel and react more calmly when adverse events occur. A lot of this comes down to their sense of control or influence over what’s happening to them.
Not only are mentally tough individuals more likely to consider challenging situations or adverse events to be an opportunity for growth but they are less likely to reveal their emotional state to others — and be less distracted by the emotions of others.
This improves these individual’s ability to rationalise what are otherwise considered unfair situations, and to work pragmatically to either avoid the likelihood of it happening again or to recover from adversity.
Downsides of being Mentally tough
For those people who believe they would hit the mental toughness measures out of the park, it is important to realise that there are downsides to possessing very high levels of the 8 Factors. Here are some of those:
1 Learning Orientation: May fail to see the significance to others, of an unsuccessful outcome
2 Risk Orientation: Can take on too much; bores easily – will often create too much change
3 Confidence in One’s Ability: Can believe they are right – even when they are wrong; Arrogant
4 Interpersonal Confidence: May appear to be poor at listening; can rely on the ‘gift of the gab’
5 Achievement Orientation: Can be intolerant of those who aren’t as committed
6 Goal Orientation: Can intimidate others with their goal orientation
7 Emotional Control: Unflappability can confuse others
8 Life Control: Can fail to see own weaknesses
Why Develop Mental Toughness?
We know that mental toughness is a psychological trait that determines how individuals respond to stress, pressure, and challenge. In short… developing your mental toughness, whether you’re studying, in business, or a professional sport’s person, will mean you cope better with life’s challenges.
For Individuals this means:
- a greater ability to bounce back from setbacks and failures and they see challenges as opportunities for growth rather than threats
- greater control over their emotions are less likely to be overwhelmed by stress, making it easier to manage high-pressure situations
- staying focused on their objectives, even when obstacles arise, leading to greater personal and professional achievements
- take on challenges with a proactive and positive mindset, which enhances problem-solving and decision-making
For Teams this means:
- individual members can remain calm and composed under pressure, improving overall group performance
- team members can communicate more effectively and support each other, fostering a positive and productive work environment
- teams are more likely to collectively embrace challenge as an opportunity for growth and can navigate change and uncertainty with greater ease
📩 GET IN TOUCH to discuss how we can help you or your team strengthen mental toughness🚀.
Ready to Build Your Mental Toughness?
Mental Toughness is the key to performing at your best—whether in the workplace or everyday life. Now that you understand the power of the 8 Factors of Mental Toughness, why not take the next step in strengthening your resilience and mental fitness?
At Get Mentally Fit, we provide evidence-based tools to help individuals and teams develop mental toughness. For an individual, a great place to start is to check out our Mental Fitness Check or Leader Support services, which is facilitated by our Principal Psychologist Emily Johnson.
Take the next step today.
📩 CONTACT US to discuss how we can help you or your team strengthen mental toughness.
📖 Learn more about our Mental Fitness Check or Leader Support services.
🚀 Explore our Workplace Training Solutions and start building a high-performance, mentally resilient culture.
Let’s unlock your potential – one mindset shift at a time!


